Navigating Cybersecurity Compliance in Data Centers: A Guide for Businesses In today’s digital age, data centers are the backbone of business operations,
How to Find the Right HIPAA-Compliant Data Center for Your Healthcare Organization In the evolving landscape of healthcare technology, ensuring the protection
4 Benefits of Data Center Consolidation Many organizations transition to cloud-based solutions only to find themselves facing a highly complex computing landscape.
Colocation Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Colocation Costs If you’re new to the world of colocation services, you may have questions about
Edge Computing is having an impact on data center architecture If you’re in the tech world these days, edge computing is THE
Why MSPs Need a Data Center as a Strategic Partner Managed service providers (MSPs) are increasingly becoming the go-to solutions for companies
Exploring Cloud Repatriation Benefits for IT Infrastructure Cloud repatriation has become an increasingly important topic of discussion among IT professionals, as organizations
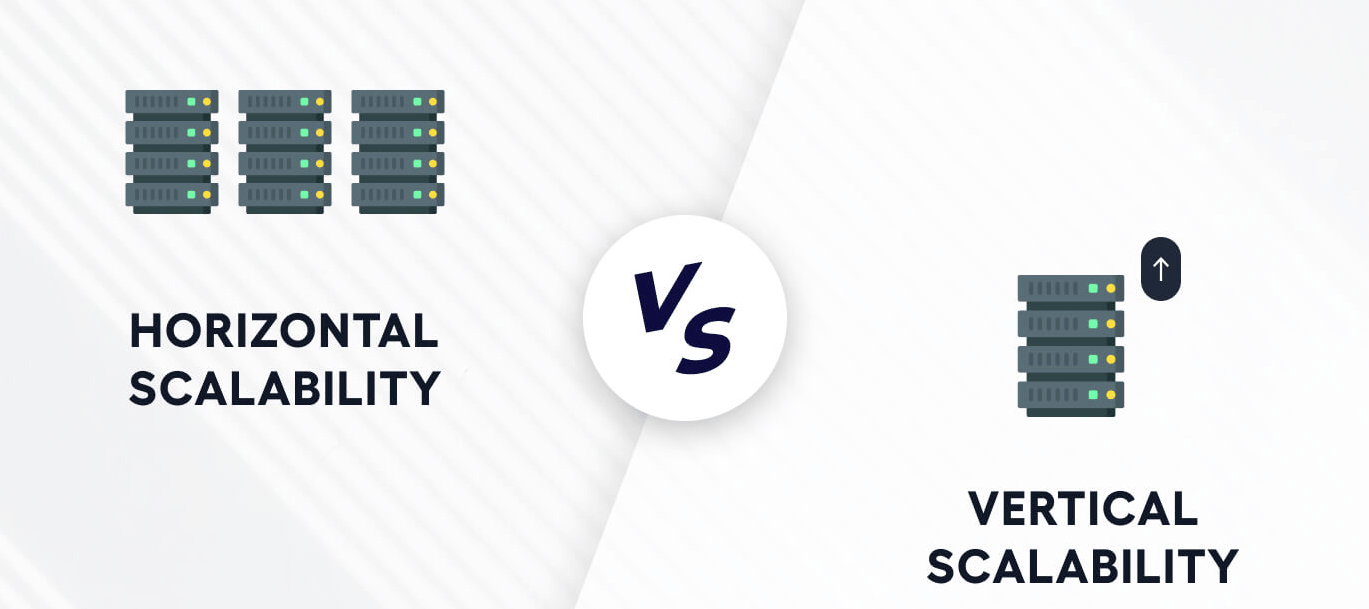
Scaling Up: Understanding the Differences Between Horizontal Vs Vertical Scaling Knowing the difference between horizontal vs vertical scaling is crucial for making
Maximizing Efficiency: The Key Benefits of Colocation Data Centers In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses across industries are increasingly reliant on
What Is a Cross Connect in a Data Center and Why It Matters? Connectivity is a crucial factor for anyone that is